CLINICAL DATA
A 10-month-old white male infant with a weight of 6.2 kg was treated in our service. At 20 days of life, congenital stenosis and cyanogenic heart disease was diagnosed originating from the left pulmonary artery (LPA). The patient was submitted to resection of the initial third of the LPA with re-implantation into the pulmonary trunk and shunting of the pulmonary-systemic flow (modified Blalock-Taussig) using a 3.5 mm2 polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft. Taking 5-mg daily of acetylsalicylic acid (AAS), the patient had a clinically adequate evolution until suddenly he deteriorated with severe cyanosis, fever and respiratory difficulties. The patient was hospitalized in a moderate general state, dyspneic, cyanotic, hydrated, and pallid, with a peripheral O2 saturation of 60%. On intubation there was no improvement in the saturation, even with an inspired oxygen fraction of 1.0. The heartbeat was regular with two sounds and a regurgitant systolic murmur at the lower left sternal border. Pulmonary auscultation was symmetrical without adventitious sounds. The liver was palpable at the right costal border and pulses were palpable in the extremities without pressure differences between the different limbs.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
The electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with a heartbeat of 150 beats per minute. The QRS complex axis was indeterminate. The PR interval was 0.12 s and the QTc interval was 0.36 s. There were signs of right ventricular overload with a pure R wave at V1 and R/S < 1 at V6. An advanced block of the right branch was seen RSR´ with a duration of the QRS of 0.16 s at V1, intrinsecoid deflection 0.08 in the right precordium. Multiphase and low magnitude complexes were seen at DII, DIII and aVF. The S wave was wide and thick at DI, V5 and V6.
RADIOGRAM
Visceral situs solitus was evidenced at levocardia. The cardiothoracic index was 0.06. Bulging of the middle arch was seen and the pulmonary vascular network was reduced in both lungs.
ECHOCARDIOGRAM
Situs solitus was evidenced at levocardia. The venoatrial, atrioventricular and ventriculoarterial connections were all concordant. A perimembranous interventricular shunt was seen, the aorta was in dextroposition, pulmonary stenosis with a maximum gradient peak of 88 mmHg as seen by Doppler color echocardiography. The pulmonary valvar annulus (PVA) was 5 mm2 in size, left pulmonary artery was 4 mm2 and the right pulmonary artery was 6 mm2, compatible with tetralogy of Fallot. An echogenic mass adhered on the wall of the right pulmonary artery with one end movable was observed without signs of perviability of the systemic-pulmonary system.
DIAGNOSIS
Considering the emergency situation and the lack of clinical improvement or correction of the metabolic changes after intubation, a cineangiographic examination was counter-indicated. The echocardiogram clearly demonstrated an obstruction in the systemic-pulmonary system of a patient suffering from anatomically complex Tetralogy of Fallot. It was unknown if the obstruction was due to acute thrombosis or infectious endoarteritis.
OPERATION
An emergency surgery was performed to correct the defect completely. As in the first procedure, a median transsternal thoracotomy was utilized and broad dissection of the adherences was necessary. Cardiopulmonary bypass was established with hypothermia at 22ºC and intermittent anterograde sanguineous cardioplegia at 4ºC. Dissection of the systemic-pulmonary shunt and immediate ligation was performed on initiation of the cardiopulmonary bypass. The graft (Figure 1), which was obstructing the right pulmonary artery due to the presence of organized fibrous tissue, was removed. The orifices of the innominate and right pulmonary arteries were sutured. The right atrium was opened and the perimembranous interventricular shunt was found. The pulmonary trunk was hypoplastic, almost atresic, with the pulmonary valve bivalved. The right ventricle outflow tract was hypertrophic.
The interventricular shunt was closed with a bovine pericardium patch and individual sutures using 6-0 polypropylene thread through an incision in the right ventricle outflow tract. This and the pulmonary branch were enlarged using bovine pericardium patches with a nº 15 monocuspid valve. The perfusion and myocardial ischemia times were 190 and 125 minutes respectively. The PTFE graft was removed and sent for laboratorial analysis from which Serratia liquefaciens was cultured, confirming the diagnostic hypothesis of endoarteritis. The patient remained in the intensive care unit for 28 days, with fever during nine days and requiring peritoneal dialysis for four days. Specific antibiotic therapy was administered for eight weeks. A future control echocardiogram demonstrated total correction of the defect and absence of images suggestive of endocarditis.
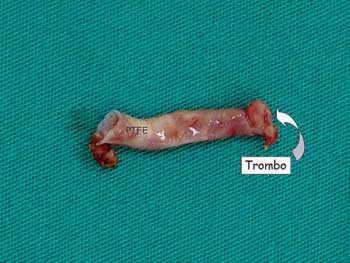
Fig. 1 - Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft with typical thrombus of infectious endocarditis at the pulmonary artery end

 All scientific articles published at rbccv.org.br are licensed under a Creative Commons license
All scientific articles published at rbccv.org.br are licensed under a Creative Commons license